Facilities Description for Research Proposals
We provide the following detailed facilities description for research proposals. These descriptions will be updated to the latest capacities and performance metrics of advanced computing resources at Clemson University, including the Palmetto Cluster.
Faculty can choose which sections to include depending on their specific proposal solicitation. However, at a minimum, we recommend the inclusion of the following sections:
Our team has prepared a copy of this information as a Microsoft Word document that you can download.
DownloadIf you would like assistance with your grant proposal or need more information than we provide here, please book a Grant Consultation appointment on our Office Hours page.
CCIT Research Computing and Data (RCD)
The Research Computing and Data (RCD) group is a centrally funded support organization inside Clemson Computing and Information Technology (CCIT). RCD provides general and advanced research computing support, training, and outreach. RCD faculty and technical staff are a highly successful group of research scientists who lead research in high-performance computing applications, high throughput computing, high-performance networking, data access and interpretation, geospatial data, visualization, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, social and biological sciences, humanities computing, and software environments for cyber-communities.
Clemson Center for Geospatial Technologies
The Clemson Center for Geospatial Technologies (CCGT) offers specialized expertise and support in geospatial research, offering comprehensive solutions to meet various GIS-related needs. The center plays a pivotal role in advancing geospatial research at Clemson University and across South Carolina through technical workshops, project support, interdisciplinary collaboration, and innovative research.
Staffing and Engagement: The center is staffed by a dedicated team of GIS experts, including full-time professionals and part-time student assistants. The team provides education and research support to the Clemson community, engaging with over 2,000 students, staff, and faculty annually through academic initiatives, research collaborations, and training programs. The CCGT team actively participates in grant collaborations, manages cloud-computing and cyberGIS platforms, and fosters partnerships with industry stakeholders to drive innovation and facilitate knowledge exchange.
Software, Computing and Facilities: CCGT’s enterprise GIS infrastructure offers geocoding, routing services, and customized web mapping capabilities for project collaboration and grant work. The center manages Clemson University’s campus-wide ESRI license, providing the research community with access to a suite of geospatial analysis, mapping, and data management tools across desktop, enterprise, and cloud platforms, all provided at no cost. The center operates a hybrid cyberinfrastructure that enables researchers to utilize high-throughput computing through the local GIS cluster (GalaxyGIS), virtual machine (VM) technologies for desktop GIS, high-performance computing via the Palmetto cluster, and cloud GIS and data services through ArcGIS Online and locally managed servers. CCGT houses a dedicated training facility, equipped with 20 student workstations featuring dual monitors, where GIS training, workshops, seminars, webinars, and customized training sessions are regularly conducted. Furthermore, CCGT maintains advanced ground-based and drone equipment for field data collection, including high-resolution imagery and point-cloud LiDAR data. The center’s team includes FAA-certified licensed drone pilots with extensive field experience.
Awards: The Clemson Center for Geospatial Technology (CCGT) was awarded the prestigious 2023 Special Achievement Award in GIS by Esri.
Information Technology Center (ITC)
The CCIT Information Technology Center (ITC) is the primary data center for Clemson University. The ITC contains 20,000 sq. ft. of raised floor space, with roughly 10,000 sq. ft. allocated for Research Computing and Data Infrastructure (RCDI).
The data center’s electrical system features two 2.5MW transformers fed from redundant power feeds. In the event of a power outage, the facility has UPS and generator backup systems, including two 2.5MW generators with a guaranteed 24-hour supply of diesel fuel on-site. Equipment in the facility is cooled by three 250-ton chillers, which produce 500 tons of cooling capacity. Only two chillers are active simultaneously, leaving the third chiller available as a reserve in case of failure. 275 tons of liquid cooling capacity is provided to RCDI through a tertiary loop, with temperature maintained through building automation and three-way mixing valves.
The ITC is the home of RCDI's hardware resources, including the Palmetto HPC Cluster and the Indigo Data Lake. The ITC is also home to the Network Operations Center (NOC), which has staff on-site 24x7x365 to monitor Clemson’s critical IT infrastructure, including RCDI resources.
High Performance Computing (HPC) - Palmetto Cluster
Clemson’s high-performance computing resources include a “condominium” style cluster, known as Palmetto 2, developed to serve the university’s wide-ranging research needs. Palmetto 2 is available to the entire Clemson community (faculty, students & staff) at no cost; faculty who purchase nodes receive priority/on-demand use of their nodes. Designed and deployed by the RCD Infrastructure (RCDI) group in collaboration with faculty researchers across the university, Palmetto 2 provides a shared platform that optimizes resources for the benefit of all users.
Named for South Carolina’s state tree, the Palmetto 2 Cluster was designed to suit many different research applications, with many powerful multi-core nodes, each with a significant amount of memory. Currently, Palmetto 2 is comprised of 1202 compute nodes (totaling over 54,476 CPU cores), and features over 300 nodes with two or more NVIDIA Tesla GPUs. These GPUs span several generations including P100s, V100s, A100s, H100s, and H200s. Additionally, Palmetto 2 provides twenty large memory nodes with more than 1.5 TB of memory. Nodes in Palmetto 2 contain both ethernet (10 or 25 Gbps) or Infiniband (56, 100, 200, or 400 Gbps) network connections. For each user Palmetto 2 allocates 250 GB of home storage as well as 5 TB of scratch space. The system, benchmarked at 3.0 petaflops, is fully backed by UPS and generator power.
GPU accelerated nodes are interconnected with high speed Infiniband networking. Palmetto 2 also contains special resources such as large-memory nodes featuring 1.5TB of RAM or more with the largest containing 6TB, and NVIDIA DGX and HGX systems for large scale AI/ML workloads.
As of July 2023, all storage for Palmetto 2 is provided by the Indigo Data Lake. Indigo is an all-flash high- performance filesystem containing 5.5PB of capacity after data deduplication and compression. 500TB of space is allocated for scratch space available on Palmetto, providing up to 5TB of space or 5 million files per user. Home directories and project spaces are also housed on the Indigo Data Lake and available on Palmetto 2.
The Palmetto 2 Cluster is housed at Clemson’s Information Technology Center (ITC). The ITC is a 24/7 monitored environment with proper power, cooling, and physical security. The Palmetto Cluster is UPS and generator backed to prevent unexpected interruptions to compute jobs.
High Performance Storage (Indigo)
Indigo is a Clemson University research data repository and processing platform. The system is backed by an all- flash scalable storage system provided by VAST Data. Indigo has roughly 3PB of raw storage, but it is anticipated to exceed 5.5PB of data leveraging data reduction and de-duplication technologies. The data lake can support large numbers of simultaneous clients by leveraging an aggregate of 1.6 Tbps of network throughput over InfiniBand and 400 Gbps over ethernet. Indigo is accessible from all RCD-managed resources via NFS, SMB, or S3 protocols. Students, faculty, and staff can access their storage via the SMB protocol over the campus network. A 500TB partition of the filesystem has been made available as scratch space to all users of the Palmetto Cluster at no charge. Each user is limited to 5TB or 5 million files, whichever comes first. This partition is automatically purged of stale data and is not intended for long-term storage. Faculty can purchase persistent storage on Indigo that also features backups and snapshots. Indigo storage owners will no longer need to copy data to scratch space before processing and can run directly against their partition.
Open Science Grid
Clemson University maintains a strong relationship with the Open Science Grid (OSG) consortium, contributing computing power to support OSG via OSPool and sending out many computing jobs to take advantage of the community resource. Clemson’s RCD team is willing to support faculty and staff interacting with OSG resources.
Research Computing Facilitation
User support is provided by the CCIT Research Computing and Data, Engagement (RCDE) team, a dedicated team who provide training and research support to Clemson students, faculty and staff. RCDE provides general and advanced research computing support, training, and outreach. RCDE staff guide the community in use of high-performance computing applications, high throughput computing, data access and interpretation, geospatial data, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, cloud computing, materials sciences, biological sciences, and software environments for cyber-communities.
PATh
Clemson University maintains a strong relationship with the PATh community, contributing computing power (17 million core hours in the past twelve months) to support the OSPool and sending out many computing jobs to take advantage of the community resource. Clemson’s CCIT team has dedicated personnel to support faculty and staff interacting with PATh resources.
Cloud Computing Resources (CloudLab)
Clemson University is one of the three major sites participating in the NSF-funded CloudLab project www.cloudlab.us. The project enables researchers to provision experimental distributed infrastructure with administrative privilege for over 1,500 computing nodes and computing resources. Clemson University hosted resources for CloudLab include a 316-node compute cluster and a 6-node storage cluster. The CloudLab cluster nodes contain a mix of Intel Xeon, AMD EPYC, and IBM Power PC architectures, and also offer a variety of co-processors such as NVIDIA Tesla GPUs, NVIDIA BlueField-2 SmartNICs, and Xilinx FPGAs. The latest expansion of the CloudLab cluster contains 32 nodes with 36-core Intel Ice Lake CPUs featuring Speed Select and SGX capabilities, and 32 nodes with 32-core AMD EPYC Milan CPUs featuring SEV capabilities. All 64 new nodes contain 256GB of RAM, NVMe local storage, and 100GbE Networking. 4 of the storage nodes contain dual 10-core CPUs, 256GB memory, 8 1TB HDDs, and 12 4TB HDDs, and 2 of the storage nodes contain dual 6-core CPUs, 128GB memory, and 45 6TB HDDs.
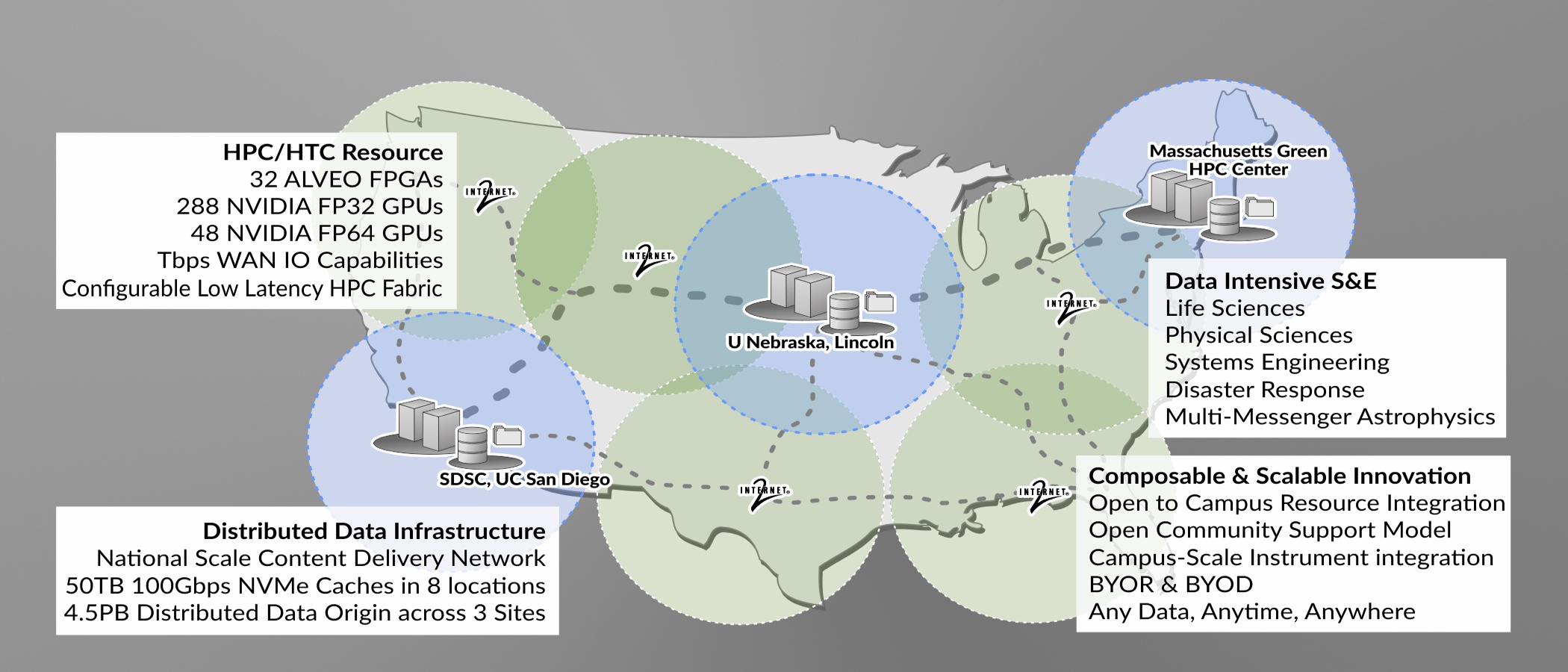
National Research Platform
The National Research Platform (NRP) (nationalresearchplatform.org) is a partnership of more than 50 institutions-including Clemson- led by researchers and cyberinfrastructure professionals at UC San Diego, supported in part by awards from the National Science Foundation. NRP is the name of the set of programs, facilities, and policies that are designed for distributed growth and expansion. NRP’s primary computation, storage, and network resource is a ~300 node distributed cluster called Nautilus that hosts many network testing data transfer nodes including ones used by the Open Science Grid (OSG). Nautilus is a powerful nationally distributed computer system with CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, in two types of subsystems (“high-performance FP64/FPGA” and “FP32-optimized”), specialized for a wide range of data science, simulations, and machine learning or artificial intelligence, allowing data access through a federated national-scale content delivery network.
Fabric
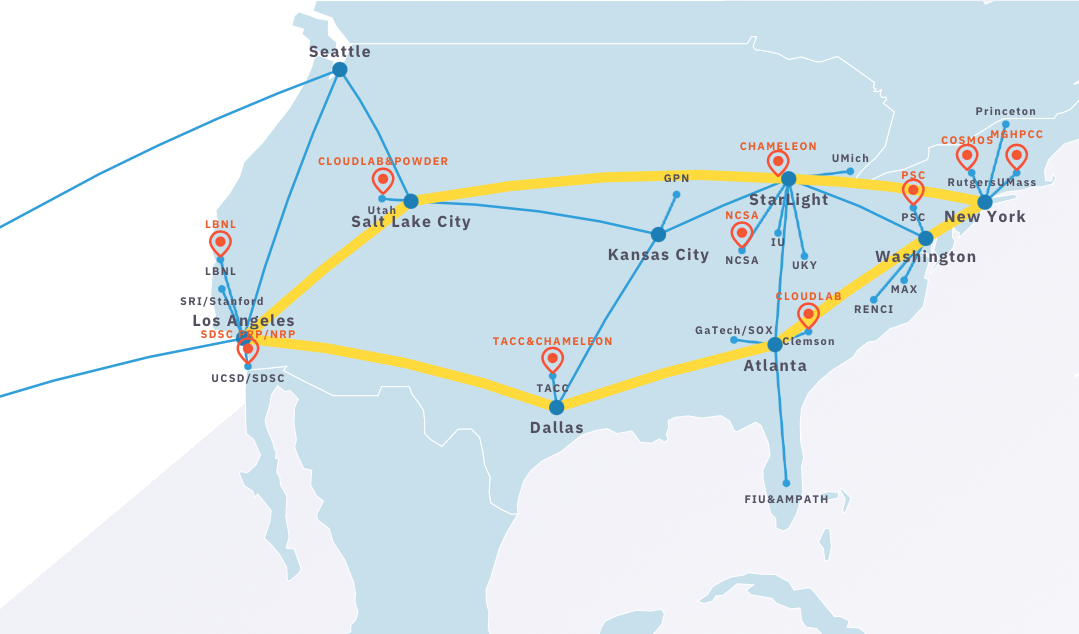
FABRIC (FABRIC is Adaptive ProgrammaBle Research Infrastructure for Computer Science and Science Applications) is an International infrastructure that enables cutting-edge experimentation and research at-scale in the areas of networking, cybersecurity, distributed computing, storage, virtual reality, 5G, machine learning, and science applications.
The FABRIC infrastructure is a distributed set of equipment at commercial collocation spaces, national labs and campuses. Each of the 29 FABRIC sites has large amounts of compute and storage, interconnected by high speed, dedicated optical links. It also connects to specialized testbeds (5G/IoT PAWR, NSF Clouds), the Internet and high-performance computing facilities to create a rich environment for a wide variety of experimental activities.
Networks
At the core of Clemson’s local area network are two fully redundant, 100 Gbps-connected Juniper QFX10008's. These have multiple 40 Gbps-connected links to Cisco Nexus 7700's in diverse campus locations. The Nexus switches aggregate dual 10 Gbps connections from Cisco 9300 switch stacks that serve as building network distribution and access switches. The multi-gigabit Cisco 9300s allow end user connections of up to 5 Gbps. This network design has zero single points of failure in the core and distribution layers, is consistent across Clemson’s entire campus, is easy to troubleshoot, and behaves deterministically, should link or equipment failure occur.
The SC-REN Network is Clemson University’s upstream connection to the national research community via direct fiber between Clemson, Atlanta, and Charlotte. SC-REN connects to Internet2, a national high-speed research and education network in Atlanta and Charlotte, including a dedicated 100Gbps connection to Internet2's Advanced Layer 2 Service (AL2S) network, to provide Clemson University's research community high speed and redundant connections for their research needs. SC-REN currently provides over 160Gbps upstream capacity to its membership with geographically redundant connections in Atlanta, Charlotte, Clemson, Anderson, and Columbia. SC-REN’s network brings Clemson the technological infrastructure that faculty and researchers need to collaborate nationally and internationally with colleagues and access resources.